Understanding user behavior and preferences is crucial for anyone working in the field of UX research. With technology advancing so rapidly, AI tools have emerged as powerful assistants in this area. However, it’s important to balance their usage to ensure that they support and not replace the human element in UX research. As we go through the intersection of technology and UX research, artificial intelligence presents both opportunities and challenges. The key lies in leveraging AI to enhance our capabilities without overshadowing the irreplaceable insights that come from direct human understanding and empathy.
The Importance of User Insights in UX Research
Understanding the User
To craft a product that resonates, we must first deeply understand who our users are. This involves collecting comprehensive data on their behaviors, goals, and challenges, forming a foundation for all design decisions. How can we be sure that the data we are collecting is relevant to our users? Here is where we need to talk about “personas.” We can borrow the definition from one of our other articles, “21 Terms Everyone in the UX Design Industry Should Know“:
“A persona is a fictional representation of a user group. It encapsulates their characteristics, behaviors, goals, and needs, aiding in designing for specific user segments. Personas humanize the user base, enabling designers to design for specific user needs and goals. This results in more relevant and impactful user experiences.”
So to collect relevant, actionable data, we need to build personas and recruit participants for our studies that match those characteristics. If you are not sure how to recruit participants for your UX research or study, you can tap into Useberry’s participant pool to recruit the right users effortlessly.
Uncovering User Needs and Preferences
Considering that we have our study objectives and know what our personas look like, the next step is to set up the study. We could utilize tools such as ready-made professional templates from Useberry to expedite the study-building process and avoid the need to start from scratch every time.

Now that we have set up a study based on our objectives and found participants that represent real users, we can start collecting our data. However, understanding user needs and preferences isn’t just about asking the right questions and gathering data; it’s about interpreting the answers in a way that guides actionable insights. This is where the depth of human analysis plays a critical role, and the capabilities of AI may be lacking.
The Role of AI in Enhancing User Insights
AI can swiftly process vast amounts of data, identifying patterns that might take humans much longer to see. This accelerates the research phase, allowing UX professionals to focus on creative solutions to user problems. There are many risks and rewards involved with using AI for generating user insights from your UX research data, which we will cover in this article.
AI-Powered Tools in UX Research
Leveraging AI for Data Analysis
AI excels at sorting through data and highlighting relevant trends. This capability can significantly enhance the efficiency of UX research, providing a quick turnaround on user insights. However, can we really trust the insights that AI provides? If you’re using them for their proven purpose, which is to save time, I would say “yes.” AI tools are being marketed as “solutions,” which obscures their true value as significant time savers. While AI can expedite your journey, it cannot fulfill your tasks entirely.
The allure of AI may attract many SMEs or start-ups to automate data analysis and insight generation processes to save time and resources, but ironically, this is the area where AI is least effective. The larger and more general a problem is, the more likely it is for an AI tool to identify it. As we get to more specific data sets and niche markets, AI’s ability will diminish due to its dependence on the training data. So presenting AI as a miracle solution is a major disservice to any business working on finding a solution to a usability issue or a problem that you can consider rare or “unique.” These outlandish claims to get quick adoptions hurt the level of trust that AI companies need to build gradually with users over time.
AI Tools for User Feedback Analysis
Feedback analysis tools powered by AI can quickly categorize and summarize user feedback, which helps in rapidly identifying areas needing attention. AI tools designed for analyzing user feedback typically utilize natural language processing and machine learning to automate the categorization and sentiment analysis of textual feedback. These tools are capable of processing large volumes of data much faster than manual methods, helping teams quickly identify common themes and user sentiments.
NLPs are similar to LLMs, which have become very popular through OpenAI‘s ChatGPT in recent years, but they are broader. NLP involves the ability of a computer program to understand and analyze human language as it is spoken or written. Speech recognition systems could be very useful for analyzing recording sessions from UX studies, but translation services and sentiment analysis are some of the other main categories that can utilize NLP technologies.

Implementing Natural Language Processing in User Research
Natural Language Processing technologies can interpret open-ended responses at scale, providing richer insights into user sentiment and needs. Some of the primary applications of NLP technologies for research tools are:
- Text Analytics Platforms: These tools analyze text data from surveys, social media, and other feedback channels to extract useful information about user opinions and preferences.
- Sentiment Analysis Tools: By evaluating the tone and emotions behind user comments, these tools help in understanding the positive, negative, or neutral sentiments associated with the product.
- Theme Detection Systems: They automatically detect recurring themes or topics in user feedback, enabling UX researchers to focus on areas that require attention or improvement.
Based on the above, it is clear that NLP technologies are very promising for building tools that can analyze user interviews or go over the interview transcripts. Let’s take a look at the benefits and drawbacks of AI-generated as a whole:
The Benefits of AI-Generated Insights
Unlike human analysis, AI provides consistent results without the fatigue or bias introduced by manual processing.
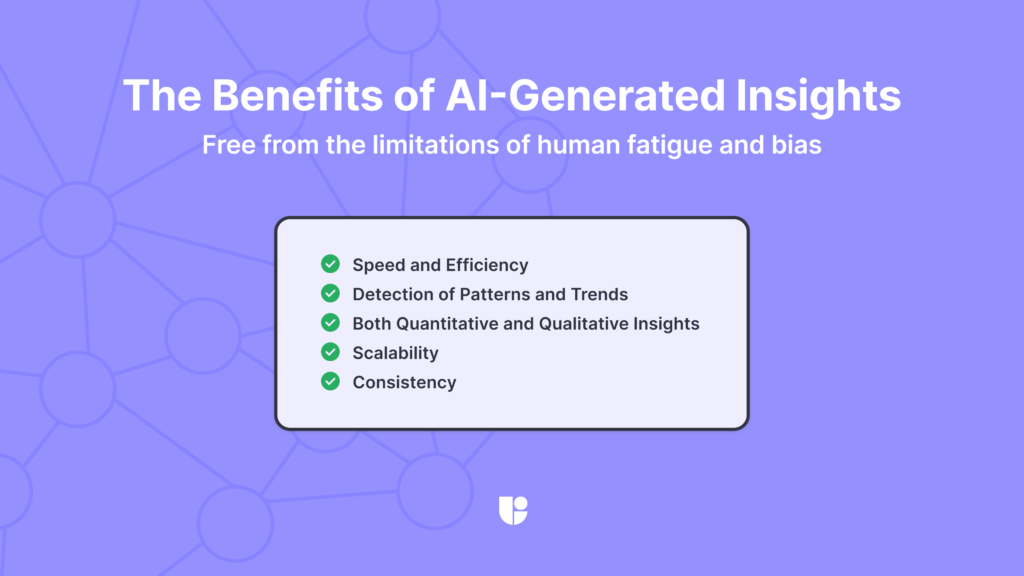
- Speed and Efficiency: AI can analyze data much faster than human analysts, allowing for the rapid generation of insights. This speed is particularly useful in environments that require quick decisions or have too large data volumes for manual analysis. Listening to recordings of every real user could be an unimaginable task for a researcher but an AI assistant can summarize it quickly.
- Detection of Patterns and Trends: AI algorithms excel at identifying patterns and trends in data that might not be immediately obvious to human researchers. This can lead to the discovery of new user behaviors or preferences that can inform design decisions.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Insights: With advancements in AI, tools can now provide both quantitative data analysis and qualitative insights, such as sentiment analysis. This dual capability allows for a more holistic understanding of user experiences.
- Scalability: AI systems can handle an increase in data volume without a loss in performance. This scalability makes it easier for organizations to expand their research scope without additional investments in human resources.
- Consistency: AI tools operate with a level of consistency that removes some human errors or biases from the analysis process. This can be crucial in ensuring that the insights generated are reliable and can be used to make informed decisions.
The Drawbacks of AI-Generated Insights
Ok, at this point, I am sure you are wondering why I had a pessimistic tone earlier, because so far everything sounds great. So now let’s take a look at some of the main drawbacks of depending on AI-generated insights:
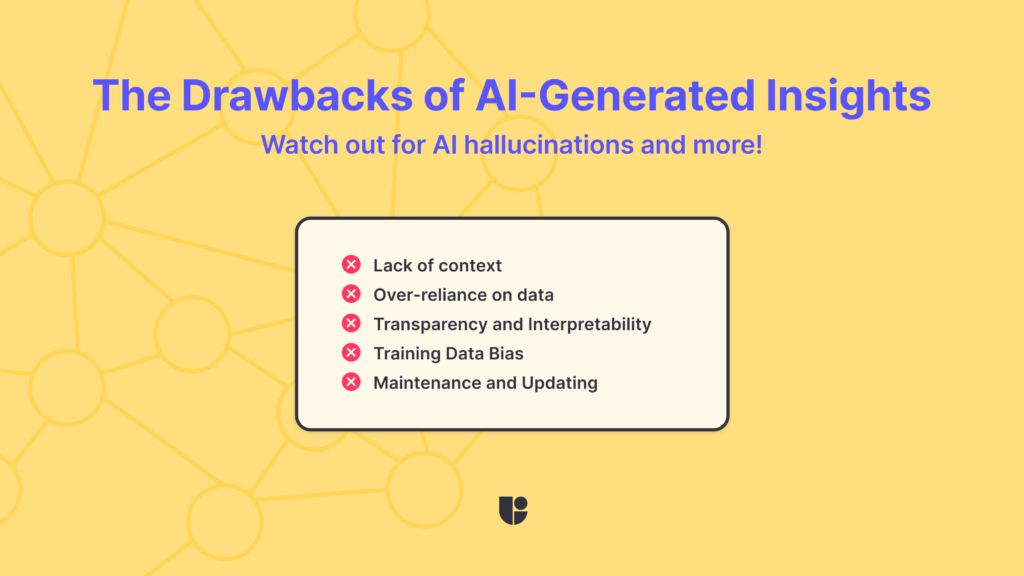
- Lack of context: AI may miss contextual cues that human analysts would naturally understand. This can lead to misinterpretations of the data, especially in complex scenarios that require deep cultural or situational awareness.
- Over-reliance on data: There’s a risk that reliance on AI for insights could lead organizations to focus too heavily on data-driven decisions, potentially neglecting innovative ideas that do not immediately align with what the data suggests.
- Transparency and Interpretability: AI models, especially those based on deep learning, can sometimes act as “black boxes,” where the reasoning behind certain decisions or insights isn’t clear. This lack of transparency can be a barrier in environments that require full accountability.
- Training Data Bias: The insights generated by AI are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased or limited, the insights will likely be biased or limited too, which can lead to skewed, unfair, or unprecise insights.
- Maintenance and Updating: AI models require continuous updates and maintenance to stay relevant as user behaviors and environments change. This ongoing requirement can be just as resource-intensive as manually going through data.
While AI tools can generate basic insights into user behavior and preferences, human researchers should still provide a more nuanced understanding. There’s a risk of over-reliance on these AI systems in critical decision-making processes, which can be problematic given their potential for errors and biases. Better transparency and representing the capabilities of AI in a more realistic way would lead to more effective ways of implementing AI in UX research in the future.
Overcoming Challenges and Ethical Issues in AI-Driven UX Research
Addressing Human Biases and Potential Biases in AI Models
It’s crucial to monitor both human and AI biases in research tools to ensure that the insights generated are valid and fair. AI models can inadvertently introduce or amplify biases if not carefully managed. Some of the most common biases that might occur in AI models used in UX research include sampling bias, interaction bias, confirmation bias as well as historical bias, and algorithmic bias. If some of these biases appear familiar, it is because they are the same ones that can result from human researchers’ studies and insights. Don’t forget that AI is trained on data that is generated by humans, so any bias that exists in that data would also be present in the AI model as well. Recently, some of the most popular generative AI models had some hilarious results while trying to correct racial bias in their training data.
Addressing these biases involves several strategies, including diversifying training data, implementing rigorous testing phases to identify and correct biases, and maintaining transparency in how AI models generate insights. It’s also crucial to have a diverse team involved in the development and deployment of AI tools to provide multiple perspectives on potential biases and their impacts. This proactive approach ensures that AI-supported UX research is fair, equitable, and truly representative of all user groups.
Privacy Concerns in AI-Enabled User Research
Since the technology often processes large amounts of personal information, privacy concerns about using AI to analyze user data are increasing. To protect user information, AI must always comply with privacy laws and ethical standards when gathering and analyzing user data. However, there are still some concerns when it comes to AI data analysis, such as:

- Data Collection and Consent: A major privacy concern is the extensive data collection capabilities of AI systems, which often collect more data than users realize. Ensuring that user consent is both informed and genuine is a challenge, as users may not fully understand what data is being collected or how it will be used.
- Data Persistence and Repurposing: After collection, data frequently stays in systems for longer than necessary, potentially leading to misuse. Additionally, repurposing data initially collected for one purpose without additional user consent could result in privacy breaches.
- Data Spillovers: Data collected for specific purposes might inadvertently become exposed beyond the intended scope, leading to unintended privacy breaches in interconnected systems.
- Profiling and Privacy Harms: AI’s capability to profile individuals can lead to “predictive harm,” where sensitive attributes about individuals are inferred from unrelated data. This can make privacy concerns worse, particularly when such profiling leads to group stereotyping or discrimination.
Ethical Considerations in Using AI-Powered Research Tools
Ethical use of AI involves transparency about how data is used, ensuring that users are aware and consent to their data being utilized in research. As AI becomes a part of our daily lives, it brings a host of benefits. However, this rapid integration also reveals significant gaps in both how well users understand the technology they’re interacting with and how our legal systems struggle to keep pace. Some of the major ethical concerns include:
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases, which may lead to discrimination, especially in critical applications such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. Ensuring that AI systems are fair and unbiased remains a significant ethical challenge.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: The use of AI in surveillance technologies, such as facial recognition systems, raises serious privacy concerns and debates about the balance between security and individual freedoms.
- Transparency and Control: The need for transparency regarding the operation of AI systems and the use of data is increasing. Often, users lack control over their personal information, and the opaque nature of some AI technologies makes it difficult for people to understand and challenge decisions made by AI.
- Economic Inequality and Access to Privacy: Economic inequality can lead to incomparable levels of data protection, where individuals with fewer resources are more vulnerable to privacy breaches.
- Security Risks and Data Breaches: The expansive use of AI increases the risk of cyber threats and data breaches, highlighting the need for robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
Just like when sharing the capabilities of AI insight tools, ethical AI development should prioritize transparency, fairness, and accountability to mitigate these risks and protect user privacy in AI-enabled research to tackle current issues and protect against future issues.
Future Trends and the Role of AI in UX Research

Emerging AI-Based Methods for User Research
I don’t want to lead to the conclusion on a negative note, because it is not all doom and gloom. New AI technologies are constantly being developed that promise to further refine the accuracy and efficiency of user research while mitigating the potential risks.
UX research is growing with the integration of AI, which offers new ways of analyzing data and understanding user behavior. These emerging AI-based methods are enhancing the way we gather and process user data, enabling researchers to uncover complicated, harder to see patterns that may go unnoticed through traditional techniques. This shift towards data-driven strategies is setting the stage for more nuanced and effective user experience design. We just have to remember that AI is a tool to assist us, not replace the human element.
Predictive Analytics and AI-Driven Personalized Experiences
Predictive analytics, enhanced by AI, are shaping the future of personalized user experiences. These tools use historical data to predict future behavior, allowing designers to anticipate user needs and craft experiences that are more aligned with individual preferences. The use of AI in predictive analytics represents a significant leap forward in our ability to tailor digital environments to user specifics, thus enhancing engagement and satisfaction. With these models, we might have insights to predict user needs even before they arise and develop products to satisfy those needs as they become apparent.
This type of AI opens a whole new avenue in UX research, where we will be looking for insights from user experiences that are going to appear in the future to develop products today.
The Potential of AI in Transforming the Design Process
AI’s capability to process and analyze data quickly can significantly impact the UX design process, making it more agile and responsive to user needs.
AI has the potential to revolutionize the UX design process by facilitating swifter and more accurate iterations. With its ability to quickly analyze large datasets, AI supports designers in making informed decisions swiftly, reducing the time from concept to implementation. This not only increases the efficiency of the design process but also allows for a more dynamic approach to adapting user feedback into ongoing design enhancements.
Each of these trends illustrates AI’s growing influence in UX research and design, promising a future where technology and creativity converge to create more responsive and user-centered products. As we continue to explore and integrate these capabilities, the potential for AI to revolutionize the field remains vast and expanding.
Conclusion
Despite the impressive capabilities of AI, it is crucial to keep the human element at the forefront of the design process. Just as with other areas discussed in this article, key takeaways are ensuring that there is a human at the helm, guiding, making decisions, and providing creative direction is essential. This balance ensures that AI tools enhance rather than replace the human touch, preserving the creativity and empathy that only humans can bring to user experience design.
By embracing these advancements while maintaining human oversight, AI can be leveraged to not only speed up the design process but also enrich it, ensuring that the end products remain user-centric and innovative.
Reach out to us today!
Would you like to know how Useberry can support your UX research and design process?